When it comes to growing herbs, rosemary is often regarded as a versatile and fragrant…
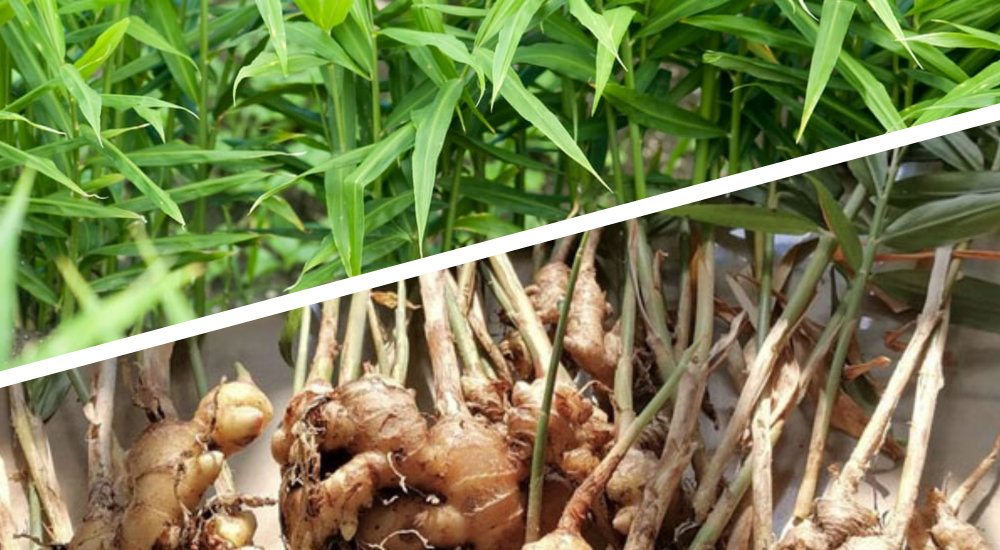

Where Does Ginger Grow Best? Ideal Growing Conditions
Ginger, with its unique flavor and numerous health benefits, is a popular ingredient in cuisines and herbal remedies around the world. But have you ever wondered where ginger grows best? In this blog post, we will explore the ideal growing conditions for ginger and uncover the secrets to cultivating this versatile spice in your garden.
Understanding Ginger
Ginger (Zingiber officinale) is a tropical herbaceous perennial plant that belongs to the Zingiberaceae family. It is native to Southeast Asia and has been cultivated for thousands of years. Ginger is prized for its aromatic rhizomes, which are used in cooking, herbal medicine, and even as a natural remedy for various ailments.
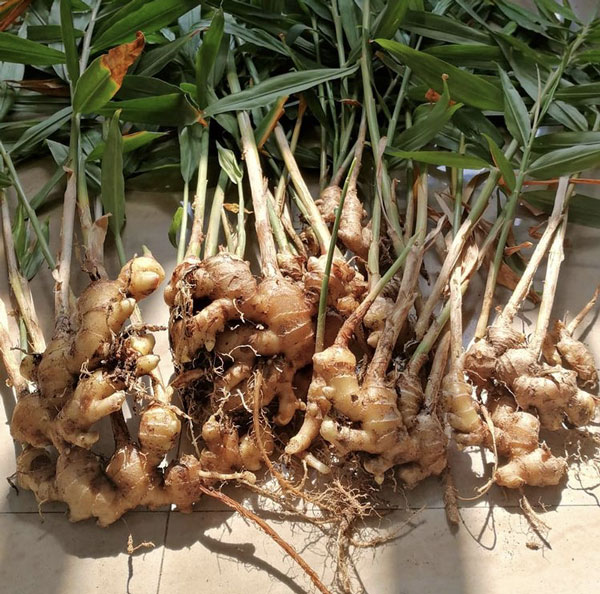

Optimal Growing Conditions for Ginger
To ensure successful ginger cultivation, it is essential to provide the plant with the right growing conditions. Here are the key factors to consider:
- Climate: Ginger thrives in warm and humid climates, typically preferring temperatures between 75°F to 85°F (24°C to 29°C). It requires a frost-free environment, as exposure to cold temperatures can damage or kill the plants. In its natural habitat, ginger grows best in tropical and subtropical regions.
- Sunlight: While ginger prefers partial shade, it still requires a good amount of sunlight. Ideally, it should receive about 4 to 6 hours of indirect sunlight per day. Avoid exposing ginger plants to intense, direct sunlight, which can scorch the leaves.
- Soil: Ginger prefers loose, well-draining soil that is rich in organic matter. It thrives in slightly acidic to neutral soil with a pH range of 6.0 to 7.0. Additionally, incorporating compost or well-rotted manure into the soil can improve its fertility and drainage.
- Watering: Ginger requires consistent moisture to grow properly. Keep the soil evenly moist but not waterlogged. Avoid overwatering, as it can lead to root rot. During the growing season, provide regular deep watering, and reduce the frequency during the dormant period.
- Planting and Spacing: Ginger is typically propagated from rhizomes, which are underground stems. Choose fresh, plump ginger rhizomes for planting. Plant them in a shallow trench, approximately 2 to 4 inches deep, with the buds facing upward. Space the rhizomes 8 to 10 inches apart, allowing room for growth and proper air circulation.
- Fertilization: Ginger plants benefit from regular fertilization. Prior to planting, incorporate organic matter or a slow-release fertilizer into the soil. Additionally, providing a balanced organic fertilizer every few weeks during the growing season can support healthy growth.
- Mulching: Applying a layer of organic mulch, such as straw or wood chips, around ginger plants helps retain soil moisture, suppresses weeds, and regulates soil temperature. Mulching also enriches the soil as it breaks down over time.

Conclusion
While ginger is native to Southeast Asia, it can be successfully cultivated in other regions with similar climatic conditions. Providing warm temperatures, indirect sunlight, well-draining soil, consistent moisture, and proper care will help ensure optimal growth and yield. Whether you live in a tropical climate or are creating a suitable microclimate in your garden, growing ginger can be a rewarding experience, allowing you to enjoy the fresh, aromatic rhizomes and incorporate them into your culinary creations and natural remedies. So, why not embark on the journey of growing your own ginger and unlock the secrets of this remarkable herb? Happy gardening!


This Post Has 0 Comments